|
Leachate treatment |



|
University of Padua IMAGE Department |
|
v The high content of organic carbon and ammonia nitrogen together with the variability in the composition of solid waste landfill leachate makes it difficult to design one tratment system consisting in a single process v Various combinations of different processes are usually used, each with the object of removing specific pollutants from the leachate |
|
Leachate treatment systems |
|
Biological treatment • Very effective methods of reducing significantly biodegradable organics as BOD5 and the main part of COD • Effective way to oxidize ammonium to nitrate by nitrification and to denitrify the nitrates to gaseous nitrogen • Organics are converted to a high degree to CO2 and water • Generally less costly than chemical/physical processes |
|
Biological systems can be distinguished in : |
|
• anaerobic biological treatment |
|
Ø parts of the landfill body used as reactor Ø anaerobic sludge bed reactor (UASB) |
|
Anaerobic leachate treatment is an effective process but remaining BOD5 and COD effluents are still high. After the anaerobic treatment step the leachate has to be treated by means of aerobic and chemical-physical processes. |
|
• aerobic biological treatment |
|
Ø earated lagoons Ø activated sludge process Ø rotating biological contactor (RBC) Ø trickling filter |
|
Physico-chemical treatment |
|
Ø activated carbon adsorption Ø reverse osmosis Ø precipitation/flocculation Ø chemical oxidation Ø evaporation Ø stripping |
|
• physico-chemical treatment should be accompanied by biological treatment for removal of easily degradable organic substances, especially in leachates from young landfills • physico- chemical treatment deals mainly with removal of organic substances which are refractory to biostabilization • physical processes in various combinations are among the most suitable in treating both “young” as well as “old” leachate |
|
Leachate treatment plant in a sanitary landfill |
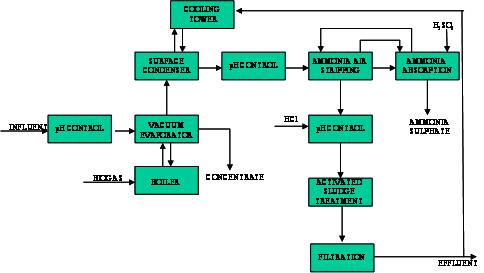
|
(from Depuracque Servizi S.r.l.) |
|
Steps of leachate treatment 1. Vacuum evaporation: at controlled pH it is able to produce an effluent almost without dissolved solids, heavy metals and non volatile organic compounds 2. The concentrate is pumped out, collected and disposed of in the landfill 3. The acqueous phase is condensed in a surface heat exchanger with a closed cooling water system and conveyed to a pH control 4. Air stripping of the condensate in order to obtain the complete removal of ammonia 5. The gaseous flow, containing most part of the NH4, is fed to an absorption tower in countercurrent with a sulphuric acid solution obtaining ammonium sulphate 6. The condensate is conveyed to a SBR activated sludge treatment 7. The SBR effluent is submitted to a process of sterilization (utilization of sodium hypochlorite followed by sand bed and activated carbon filtration) 8. Part of the effluent is discharged into surface watercourses, part is sent to the water cooling system 9. After thickening, the waste sludge is conveyed and disposed of in the landfill |
|
Leachate treatment plant in Chianni (PI), Italy (from Depuracque Servizi S.r.l.) |
|
Leachate treatment plant in Rosignano Solvay (LI), Italy (from Depuracque Servizi S.r.l.) |

