|
Gas quantities |



|
University of Padua IMAGE Department |
|
Gas potentials of waste Theoretical calculations by Buswells equation: CnHaOb + (n a/4 b/2) ฎ (n n/2 a/8 + b/4) CO2 + (n/2 + a/8 b/4) CH4 Measured: 450 m3 CH4 / ton VS (volatile solids) 60 m3 CH4 / ton wet waste (50% moisture) Measurements at actual landfills |
|
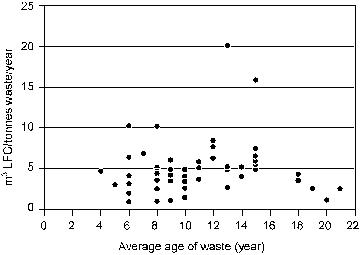
Maximum over life-time: 120 m3 gas / ton waste (50% CH4 in gas) |
|
Models for LFG at actual landfills |
|
Modelling landfill gas production Statistical analysis: when a large number of data are available, but knowledge of the system is inadequate, and the data are collected for different porpuses; this kind of model does not assume any cause-effect relation or deal with the temporal dynamics of the system, but the general characteristics of the data population and provides correlations Stochastic model: describes the temporal trend of data without explaining the same; this kind of model is useful for describing the behaviour of a black-box system; it states simply which is the output related to a specific input Semplified deterministic model: requires knowledge of the mechanisms governing the system; it is able to describe the behavior of the system with semplfied mathematical equations Complex deterministic model: acts in a similar way to the above-mentioned model using more complex mathematical equations Structure of LFG production models Theoretically a complete biogas model should include three submodels: Stoichiometric submodel: gives the maximum theoretical yield of biogas from the anaerobic degradation of the organic waste fraction . Some models proposed in the literature are simply stoichiometric and provide as a result only information on LFG yields Kinetic submodel: is a dynamic model, which gives as a result the temporal evolution of LFG generation rates. It can be either an empirical model, based on a more or less simple equation of a defined order; or a deterministic model, based on a set of equations describing the degradation of the different biodegradable MSW fractions; or an ecological model, which describes the dynamic of microbial populations and substrata within the landfill Diffusion submodel: is a dynamic model, which describes the time and space variation of pressure and gas composition within the landfill body. LFG emission rates can be obtained, and effectiveness of the gas extraction system can be verified |
|
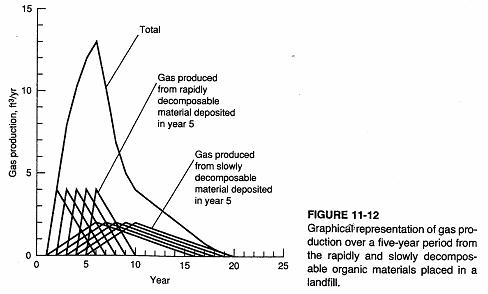
Assume easily degradable fraction and slowly degradable fraction and that filling takes place over 5 years |