


|
University of Padua IMAGE Department |
|
Functions |
|
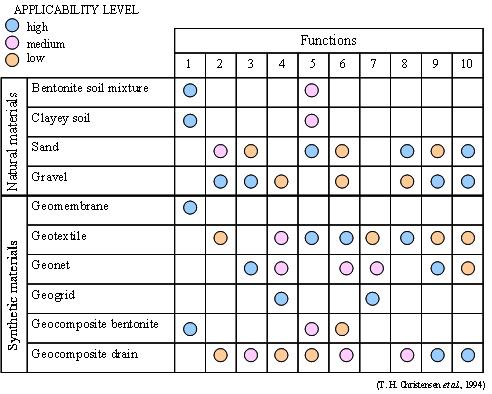
Barrier system components • Natural materials: v clayey soil v bentonite v sand v gravel • Synthetic materials: v geomembranes v geotextiles v geogrids v geonets v geocomposites Functions of barrier system components 1. Lining 2. Leachate percolation 3. Leachate drainage and collection 4. Soil reinforcement 5. Mechanical protection 6. Separation 7. Erosion control 8. Water filtration 9. Water drainage and collection 10. Biogas migration control |
|
Natural materials used in the construction of lining systems Clayey soil: is the most common natural lining material. The main factors which affect the quality of clay liners are hydraulic conductivity, degree of compaction, moisture content, clay composition, field placement technique and liner thickness. Bentonite: is a general term for indicating clay minerals capable of swelling, when wet, up to 15-18 times their dry volume. Mixtures of bentonite and sandy soil can provide a low permeability liner, particularly useful in areas where natural clay is not available. Sand: is widely used to protect synthetic liners and to increase filter stability. Gravel: is the main material for filtering and draining. The efficiency of a granular bed depends on the porosity, grain shape and strength, the rock quality (resistance to weathering and carbonate content), stability of the filter, the drainage layer thickness and general engineering of the system. Synthetic materials used in the construction of lining systems Synthetic membranes: are materials of low permeability and serve as barriers in the liner system between mobile polluting substances and the groundwater; syntheticmembranes are also used in final cover systems as barrier layers to minimize the amount of rainwater entering closed unuts. Geotextiles: are used in liner systems to provide separation between solid wastes and the leachate collection system or between the membrane and cover or embankment soils, to reinforce the membrane against puncture from the subgrade or the waste that is placed above it, and to provide filtration around collection pipes. Geonets: are grid-like products based on polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) and are used exclusively as in-plane drainage systems; they are always used with geotextiles, membranes or other materials in the planes above and below them. Geogrids: are used in the construction of waste disposal units to reinforce soils in the dikes; they are also used within landfills to steepen earth slopes or to create embankments between cells. Geogrids should not be confused with geonets which are used exclusively for drainage. Geocomposites: identify a large range of composite materials that consist of two or more geosynthetics. Drainage geocomposites are sometimes used as leachate-collection subsystems with a geotextile filter attached, but they appear to be particularly useful as surface water collectors in a landfill closure system where normal stresses are relatively low. Pipes and fittings: plastic pipes based primarily on PVC or high-density pilyethylene (HDPE) are used in constructing leachate-collection and leak-detection systems and in gas venting applications. Performance requirements of synthetic lining systems • The installed liners must have sufficiently low permeability to all constituents of the waste so that the level of constituent transmission through the lining system does not pose a threat to human health or the environment • All liner system components that may contact the waste leachate must be chemically compatible over an extended time period with the leachate to be contained • The components of a lining system must mantain their integrity on exposure to mechanical stresses • A synthetic membrane used to line a land disposal unit must be capable of being installed in such a way that it can form a continuous durable membrane • The components of a lining system need to be able to maintain their integrity and performance characteristics over the operationel life of the unit and the post-closure care period |